Cyber-physical Cooperation
As deep learning technologies increasingly integrate into transportation systems, concerns are escalating regarding the system resilience and adaptability in the face of a range of uncertainties, including variable environmental factors, fluctuating traffic conditions, and irregular distributions of road users. The development of an adaptive and autonomous traffic system through cyber-physical cooperation promises a transformative approach to mitigating such uncertainties, ensuring more resilient, safer, and equitable transportation networks.
Comprehensive traffic environment perception with edge intelligence
Motivation: The physical traffic environment, characterized by factors plays a crucial role in influencing the traffic system. Unfortunately, the neglect of these essential environmental aspects can lead to severe repercussions, especially under adverse weather conditions, including a decline in accuracy and the emergence of anomalies.
Research Summary: To mitigate the uncertainties arising from the traffic environment, we proposed an Edge-based Multi-task Safety-oriented Environmental (Edge-MuSE) sensing system. Edge-MuSE is designed to provide an extensive perception of the traffic environment, encompassing temperature, humidity, image dehazing, visibility measurement, and road surface condition classification. This innovative system is tailored for comprehensive, efficient, and cost-effective real-time monitoring, enhancing the reliability and safety of traffic management systems. (Learn more)
Multi-scale representation learning empowered crowd sensing
Motivation: As urban populations rise, the surge in road users within confined urban spaces leads to densely crowded scenarios, posing significant safety and mobility challenges for transportation systems. Sensing methods that rely on individual feature processing and analysis can be heavily compromised by occlusions, intricate backgrounds and diverse crowd density, often resulting in a marked decline in perception accuracy.
Research Summary: To address the challenges, I proposed an ensemble sensing scheme, Scale-Aware Representation Learning Empowered Sensing (SARLES) System by leveraging an innovative encoder-decoder module for the extraction and processing of both global and local texture features. Uniquely, SARLES is designed to adjust to diverse transportation settings by using a multi-scale representation learning approach to generate crowd density maps for accurate crowd counting and individual pinpointing. Pioneer tests on surveillance systems in Tokyo and Shanghai highlighted its exceptional crowd perception capabilities, achieving an accuracy rate of 93.21%. This research paved the way for transportation safety and mobility applications when the system cannot capture sufficient features for accurate sensing and perception.
Bias Mitigation in uneven distributions by integrating physical information
Motivation: Given the inherently uneven and long-tailed distribution of road users in transportation scenarios, deep learning technologies and unintentionally amplify biases, resulting in diminished accuracy for less-represented classes like children and wheelchair users. Therefore, accurately quantifying and mitigating the bias of the deep learning empowered perception system to address the proposed equity issue is a significant research focus for daily traffic services and applications.
Research Summary: In response, we conducted a trustworthy perception system based on few-shot and representation learning algorithms, DEbias Traffic Object Recognition (DETOR), for road users and traffic facilities detection and classification. By Employing DETOR, the residual neural network achieved a 290% boost in accuracy for minority transportation objects detection. The research developed a pioneer trustworthy transportation-adaptive de-biased traffic perception system, paving the way for more promising future transportation services and applications.
Integrated Sensing Technologies
Many current traffic sensing systems often face significant challenges due to the limitations of isolated sensing mechanisms, leading to not only sensor saturation and data overload, but also results in a fragmented traffic conditions awareness. Cooperative sensing technologies offer a transformative solution by integrating data from multiple sources, both within sensor unit (intra-sensor) and among various entities (inter-sensor), to enable a comprehensive understanding of traffic scenarios that enhances decision-making and improves hazard awareness.
Cooperative multi-task surveillance and connected IoT system

Research Summary: Addressing data redundancy and boosting efficiency for a comprehensive traffic scene perception, the research proposes the concept of “Sensing as a Service (SaaS)”, a demand-driven sensing scheme, and implements it to Cooperative and Comprehensive Smart Edge Node for Sensing and OpeRation (COCO-SENSOR) system. COCO-SENSOR is a cutting-edge multi-task sensing system and designed to fulfil critical real-world needs in single unit: real-time traffic and environmental monitoring, precise recognition and classification of road users, and seamless live communication among infrastructures, transportation agencies and road users, encapsulating a comprehensive approach to traffic management and safety. By incorporating advanced sensing technologies and a cooperative mechanism alongside parallel computing, COCO-SENSOR optimally allocates edge device computational resources. Implemented across three testbeds, complete with a well-developed sensor unit, mobile app, and an informative dashboard, COCO-SENSOR has demonstrated a remarkable ability to bridge the divide between sensory data and traffic service needs, achieving stellar application performance with over 95% accuracy and a consistent 30 FPS efficiency. (Learn more)
Privacy-preserving cooperation systems for cross-camera network monitoring
Research Summary: To track objects across multiple cameras and help the public agencies collect the link travel time and speed information without any sensitive privacy information, an Edge-empowered Cooperative Multi-camera Sensing (ECoMS) System is proposed. ECoMS presents a novel algorithmic and edge-server cooperative system framework to push edge computing and multi-camera re-identification workflow serving for traffic sensing based on cooperative IoT architecture. On the algorithm side, ECoMS proposes a light-weight edge-based computer vision framework for vehicle detection, tracking, and representation selection in a real-time manner. Then, by only sending the objects’ representations to the edge-server, the high-bandwidth data transmission and the heavy post-processing system can be abandoned. Further, a hierarchical clip-based deep vehicle re-identification framework is proposed and integrated into ECoMS, and significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art methods with 92.43% Rank-1 accuracy. Finally, a cooperative cross-camera traffic information estimation framework based on kernel density estimation with kernel smoother is implemented, which can get the precise and reliable cross-region traffic parameters (link travel time, speed and area OD) and distributions (less than 1.01 KL distance). (Learn more)
Distributed Machine Intelligence for Smart and Connected Systems
Distributed Machine Intelligence stands as a critical innovation for transportation systems, offering decentralized, privacy preserving, and robust processing capability that enhance safety and smart management across infrastructures.
Collaborative traffic perception and control system
Research Summary: The fusion of traffic perception and control systems facilitates a dynamic and proactive approach to traffic management, markedly diminishing congestion and enhancing traffic flow. Our research introduces the Predictive Empowered Assignment scheme for Reversible Lane (PEARL), which leverages real-time traffic sensing to enable dynamic reversible lane control, informed by short-term traffic flow forecasts. This strategy aims to optimize throughput and minimize delays. The real-time predictive control scheme employs an iterative approach, allowing the system to anticipate and plan for future traffic scenarios, thereby optimizing current lane assignments. Field experiments demonstrate that PEARL effectively boosts total throughput by 9.93%, showcasing its potential for practical implementation in contemporary traffic systems. (Learn more)
Synchronized Infrastructure System with Cooperative Engagement for Dilemma Zone Mitigation
Research Summary: The dilemma zone is a significant safety concern in transportation where existing infrastructure systems often lack the real-time processing and communication capabilities to mitigate the heightened risk of accidents caused by driver hesitation at signal changes. This research introduces an edge-server-based platform that unifies surveillance cameras, traffic signal controllers, and road users through a cooperative framework of perception, communication, and control to adeptly mitigate dilemma zone risks. This platform is structured into three core modules: a sensing module for instantaneous vehicle detection and tracking; a data processing module for trajectory data analysis and forecasting; and a communication module that facilitates immediate interaction with infrastructure and motorists. The experiment deployed in two pioneer intersections in downtown Bellevue for one week and detected 1076 dilemma events, which achieve 92.84% accuracy. The proposed edge-server based system is the first connected infrastructure system that integrates sensing, data processing and information dissemination together for the self-operating indistinguishable signal services.
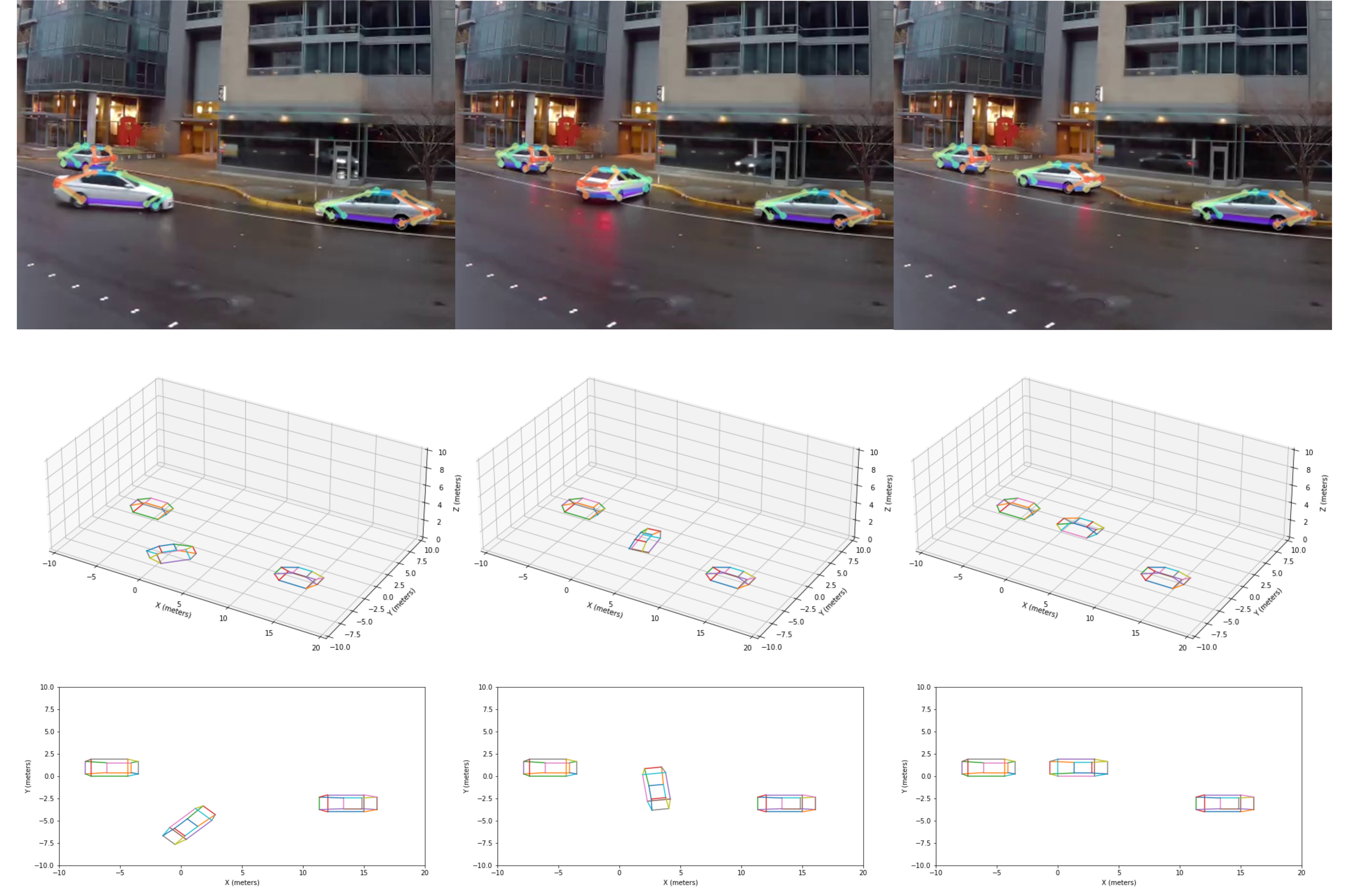
Advanced 3D Spatial Mapping for In-Depth Traffic Scene Analysis
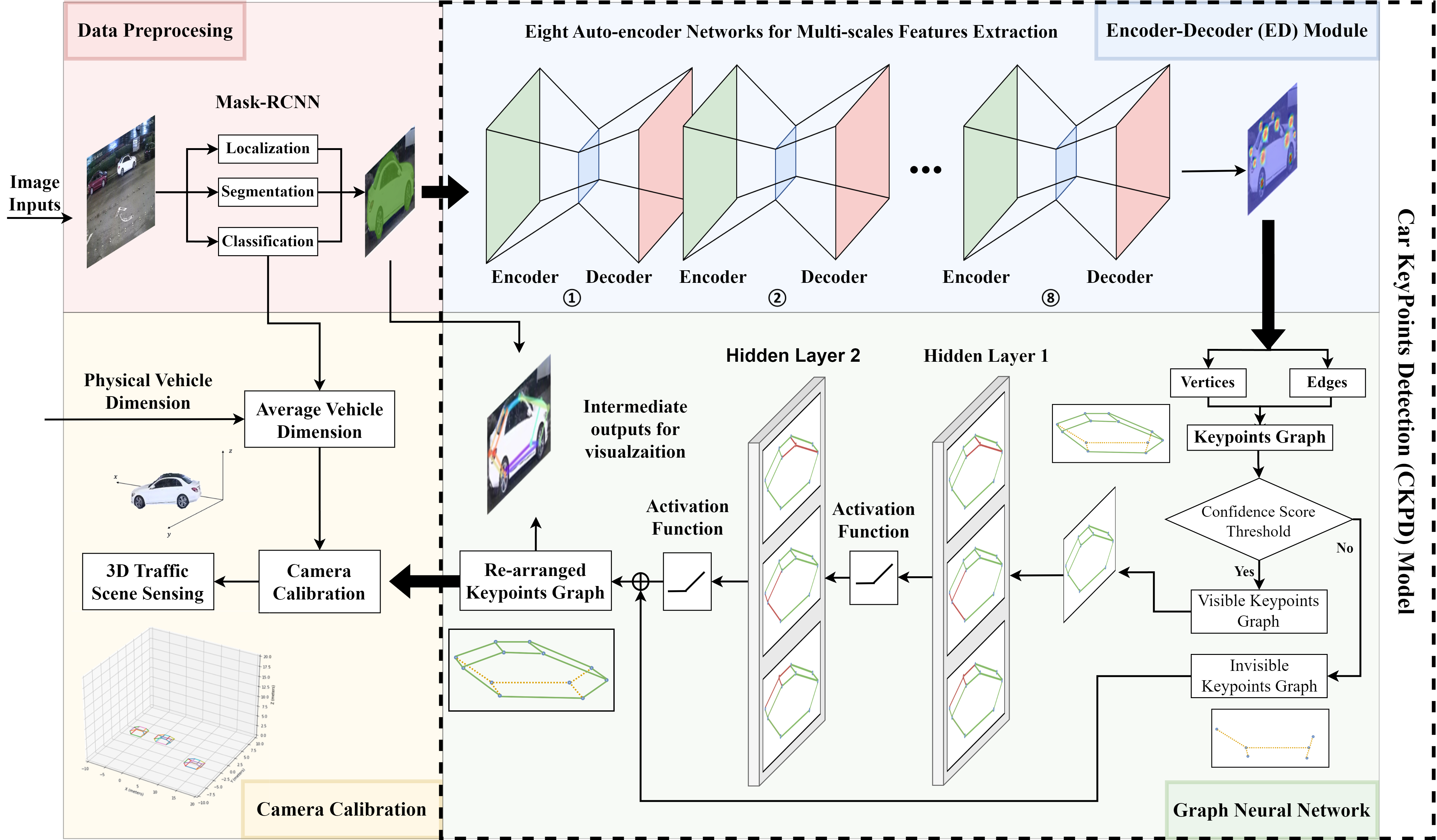
Research Summary: Advanced 3D Spatial Mapping offers a sophisticated, high-dimensional view that is essential for detailed traffic scene analysis, significantly improving accuracy in sensing spatial relationships among transportation entities. Our research introduces the 3D Structural Information Sensing System (3D-SISS), anchored by an innovative, fully automatic camera calibration technique, enabling precise real-time vehicle localization and scene reconstruction from a single monocular surveillance camera. 3D-SISS consists of a trio of integral components: a pre-processing module for detecting, classifying, and segmenting target vehicles; a cutting-edge Car Keypoints Detection (CKPD) model; and an automatic camera calibration method that accurately maps 2D keypoints into a 3D space. Field tests in the City of Bellevue demonstrate that 3D-SISS surpasses contemporary methods in vehicle localization, speed measurement, and scene comprehension, notably in dense urban settings with occlusive environments.